Top 10 Audio/Video Conferencing Security Best Practices
Apr 8, 2020
In the era of remote work, ensuring the security of audio/video conferencing is paramount. Here are the top 10 cybersecurity best practices to safeguard your online meetings.
The transition to remote work has significantly increased the reliance on audio/video conferencing platforms. As such, reinforcing cybersecurity best practices for these tools is crucial for maintaining secure and productive work environments. This guide outlines essential strategies for training employees in effective security hygiene and implementing robust security features for audio/video conferencing.
Top 10 Cybersecurity Best Practices for Audio/Video Conferencing
-
Comprehensive Monitoring and Alerting: Implement logging, monitoring, and alerting for all actions and configurations supported by your conferencing platform. Tailor these settings to meet your organization's specific security requirements.
-
Unique Meeting IDs: Avoid using personal or recurring meeting rooms. Generate a new meeting ID for each session to minimize unauthorized access risks.
-
Strong Passwords for Meetings: Secure meetings with strong passwords (at least 12 characters) and distribute these only to verified participants. Avoid sharing passwords on public forums or social media.
-
User Entry Announcements: Activate features that announce participants as they join to maintain awareness of meeting attendance and prevent unauthorized access.
-
Utilize Waiting Rooms: When available, enable waiting rooms to vet participants before granting access to the meeting, enhancing control over meeting entry.
-
Mute Participants Upon Entry: To minimize disruptions and potential eavesdropping, enable settings that mute participants as they join the meeting.
-
Restrict to Authenticated Users: Limit meeting access to authenticated users within your organization or specific guest accounts to ensure that only authorized individuals can join.
-
Video and Chat Controls: Disable video when not necessary and consider turning off private chat functionalities to reduce the risk of data leakage or inappropriate use.
-
Selective Screen Sharing: Share only specific applications or windows rather than your entire desktop, aligning with your organization's data protection policies.
-
Secure Host Controls: Keep your host PIN confidential and treat it as sensitive information to prevent unauthorized control over your meetings.
Implementing Detection and Alerting Controls
Many audio/video conferencing platforms offer advanced security settings, including detection and alerting mechanisms for unusual activities. Familiarize yourself with these features and configure them to enhance the security posture of your conferencing environment. Regularly review and update these settings to adapt to evolving security threats and organizational needs.
For specifics, we’ll cover a couple of the more popular platforms below:
ZOOM
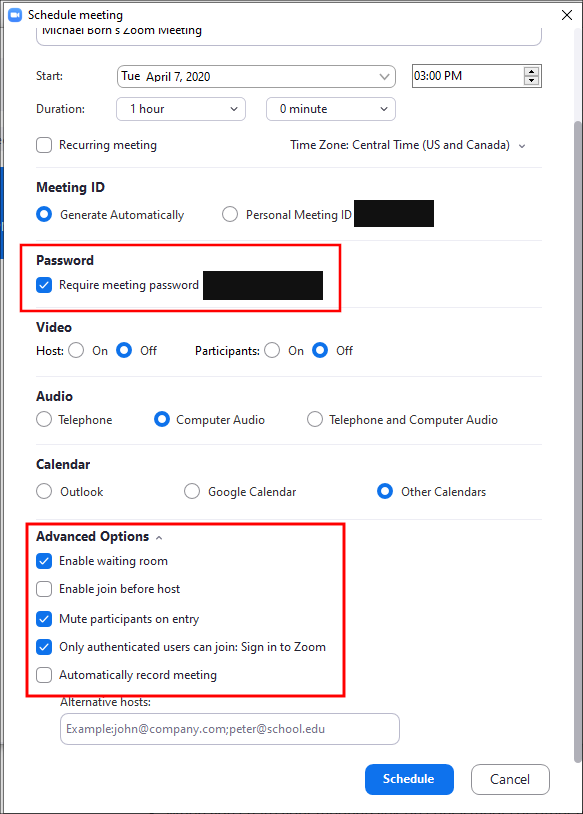
In Zoom, the “Advanced Options” area contains several settings that will help secure your meetings. In the screenshot below, we have highlighted the important settings to turn on (blue check). Nothing replaces user training however. We cannot stress enough how important it is to treat certain aspects of a scheduled meeting as sensitive data. This includes the meeting password, the meeting URL/ID and the host key. Only send the meeting URL/ID and meeting password to individuals you want to attend the meeting. We recommend protecting the host key as well.
CISCO WEBEX
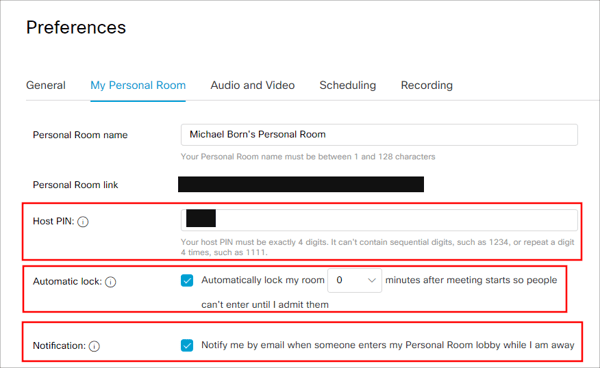
If your organization uses Cisco WebEx, there are additional options that you can configure to harden meetings which are above and beyond the default settings. It is important to note that individual users can alter their own settings, so if you have an organization WebEx administrator, it may be wise to enforce the following settings as the organization default. Uses who can control their own profile settings are recommended to use the following settings under “Preferences.” First, change the default “Host PIN.” Unfortunately, we’re stuck to using a 4-digit pin. Change this often. Second, activate “Automatic lock” for personal rooms and set them to lock immediately once the session begins.
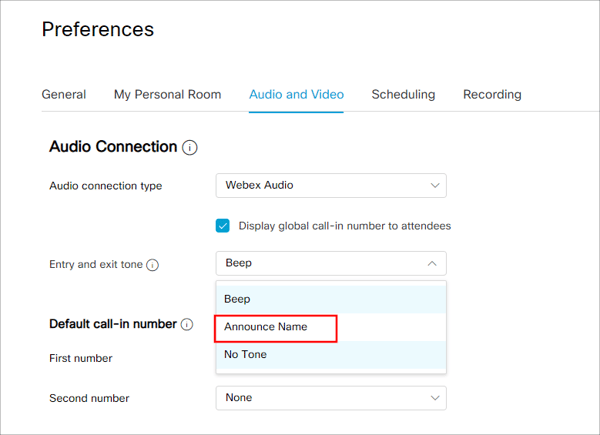
Under the “Audio and Video” settings, make sure to choose “Announce Name” under “Entry and exit tone” setting. This prompts the user to say and record their name when entering the meeting.
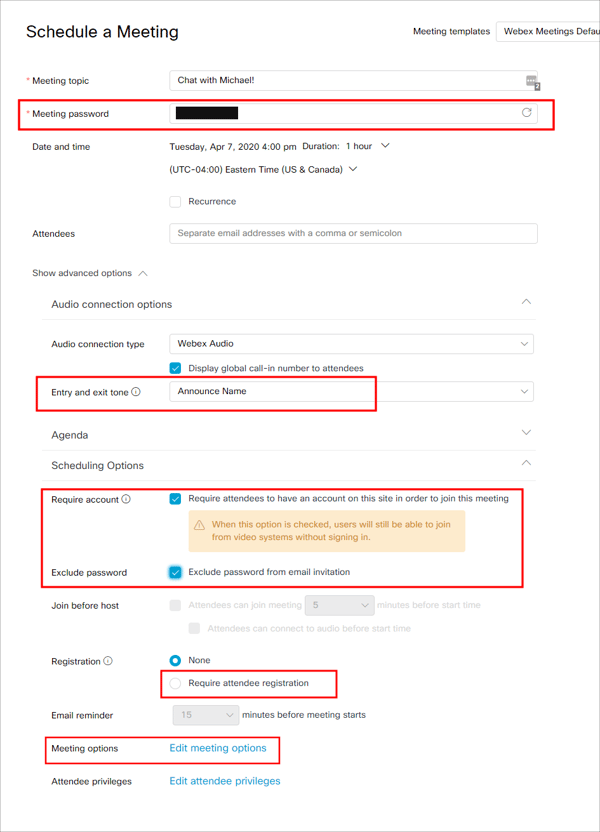
Next, when scheduling a meeting, there are additional security settings to configure. We’ve highlighted the important settings in the screenshot below. Make sure to set a strong password (minimum of 12 characters or more). One trick is to copy the password created for you, click on the regenerate icon, and then paste the copied password on the end of the newly created password. This allows you to quickly create a longer password for your meetings. Alternatively, use a password manager to quickly generate a much longer random password on the fly. If you’re hosting a public meeting, you can enable the “Require attendee registration” settings to force users to enter an email address and other information. This helps the meeting organizer validate email addresses of invited guests (assuming attendees enter accurate information of course).
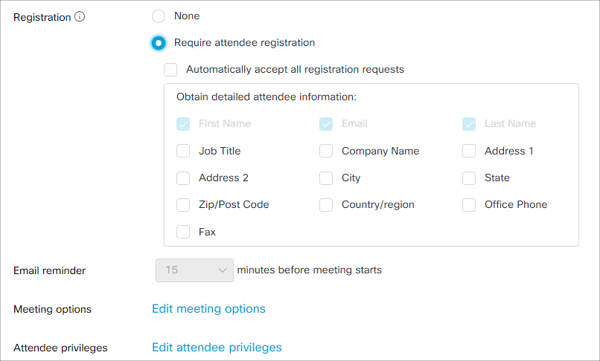
Additional meeting options allow the meeting organizer to disable chat and note taking as well to disrupt potentially malicious attendees.
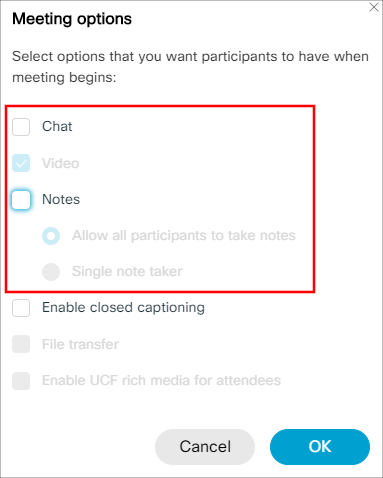
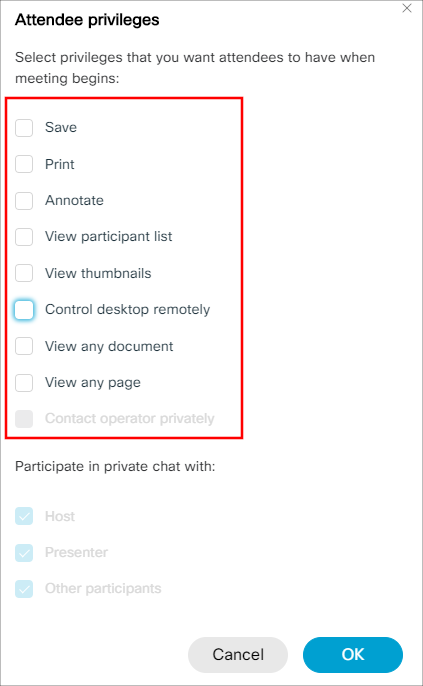
Like the “Meeting options”, the “Attendee privileges” option allows the meeting organizer to lock down the meeting even more and provide additional privilege settings for users attending the meeting.
MICROSOFT TEAMS
Microsoft Teams can create a challenge, as the hardening settings are handled in the Microsoft Teams “admin” portal. With that said, however, there are several great security settings that your organization can configure to not only harden Microsoft Teams, but to monitor and alert upon authentication and file transfers within the platform using Microsoft Sentinel.
Teams Settings
Some of the more important settings for Teams involve “External Access.” Make sure to turn the first two settings to “Off” to prevent external IM communication with external Skype for Business and Teams users, and Skype users so that chat is contained internally. If necessary, enable a whitelist of allowed domains that can join scheduled Teams meetings. Use these domains for any of your customers that need to join scheduled Teams meetings.
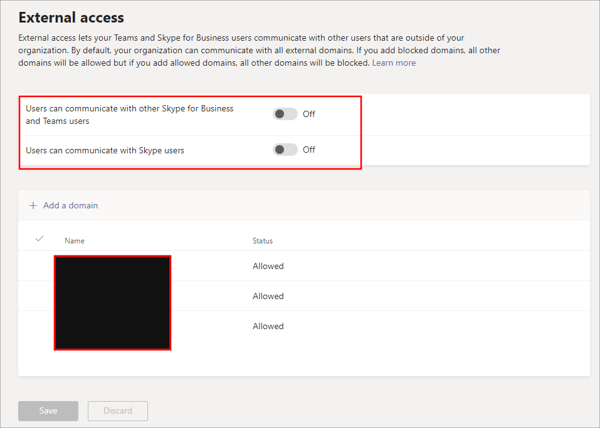
Similarly, the “Guest Access” settings dictate whether Guests can access your Teams meetings and chat.
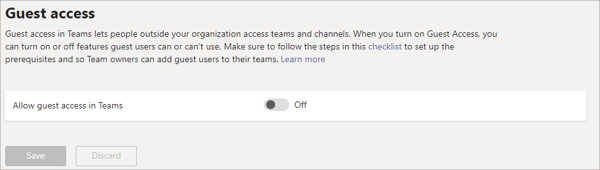
The “Teams Settings” contain additional settings that may vary from organization to organization. We recommend reviewing these settings and configuring them according to the information security policies at your organization. You’re not limited to just these settings either. Teams allows your organization to configure specific policies with very granular detail. Creating those policies is out of the scope of this blog, but we recommend using Policies in addition to the above settings to lock down your Teams platform even more.
Logging, Monitoring, and Alerting with Sentinel
In a recent post by Microsoft , Pete Bryan details some incredible functionality with MS Sentinel, Logic Apps and configuration settings to monitor Microsoft Teams. By enabling audit logging in Microsoft 365 and creating an Azure AD app to allow API access, we can have Sentinel monitor and alert on suspicious behavior within Microsoft Teams and its users. You can read the article for yourself, but I want to highlight an important piece of information from the article. You want to collect two different but related sets of logging information. First, Microsoft 365 “Audit.General” logs will capture Teams events. Second, AzureAD logs will help capture issues with Identity for Teams users. Make sure to follow Mr. Bryan’s advice on normalizing the data with KML queries too and implement some of the hunting queries detailed in the article.
No matter which of these audio/video conferencing solutions your organization uses, these top 10 steps along with end-user training will help reduce risk associated with your now primarily remote workforce.
Cybersecurity Best Practices for Conferencing
Adhering to these cybersecurity best practices for audio/video conferencing can significantly reduce the risk of security incidents and ensure that your remote work environment remains productive and secure. As the landscape of remote work continues to evolve, staying informed and proactive in implementing security measures is key to safeguarding your organization's digital assets and communications.
References
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoftteams/enable-features-office-365
https://blog.zoom.us/wordpress/2020/03/20/keep-uninvited-guests-out-of-your-zoom-event/
https://help.webex.com/en-us/8zi8tq/Cisco-Webex-Best-Practices-for-Secure-Meetings-Hosts
